BACKGROUND
Competition is an intrinsic part of an athlete’s life where anxiety is felt. The physical and cognitive components of anxiety, or “competitive anxiety”, are frequently the subject of research (Battaglini et al., 2022; Martínez-Rodríguez et al., 2022). The somatic component of anxiety refers to physical reactions that athletes may have before and also during the competition (e.g., muscle tension, stomach problems, hand tremors). Meanwhile, its cognitive component includes problems with concentrating attention, controlling thoughts, as well as worrying about how to cope during sports competitions (Martens, 1977).
Players may experience anxiety, tension, stress, and panic before or during a competition. In sports, uncertainty makes people feel anxious (Peden, 2007). Anxiety is a state of fear, worry, or nervousness. It can cause muscle weakness, a racing or intermittent heartbeat, a feeling of weakness throughout the body, fatigue, lack of strength, and even a feeling that one is about to faint. It can also cause insomnia or lack of ambition, loss of appetite or overeating, and depression. Loss of performance in sports can result from even one or two of these symptoms.
With the occurrence of COVID-19, sports players faced a huge challenge to participate in sports due to lockdown and social restrictions. Numerous competitions have been cancelled, and conducting training and competitions was significantly hampered. Limited access to sports facilities meant that athletes trained at home. They experienced uncertainty, stress, fear of infection, moral discomfort, and grief, according to studies on the COVID-19 pandemic and anxiety (Cherappurath et al., 2023; Antoniak et al., 2022). Indian and Polish athletes have faced many challenges during the pandemic. Indian athletes had to look for locations to exercise, but also ways to earn money and strengthen their motivation so as not to abandon the sport. Financial problems were mounting due to the almost four-month total lockdown. As a result, middle-class families found it difficult to support their children in sports. The lack of government and corporate support made it difficult for athletes to participate in certain sports. Athletes practised from their homes virtually via Zoom and other apps. It is worth noting that during the height of the pandemic, many sports facilities were converted into COVID care centres. Some of them were reintroduced to athletes (especially mainstream elite athletes) only in October 2020. This was demoralizing for many athletes as sports activities in India resumed much later than in other countries. Later, when sports facilities were opened to elite athletes, they practised alone or under huge restrictions such as 14-day quarantine, wearing masks, etc. (Bhattacharya, 2020). Polish athletes faced similar restrictions when the quarantine was announced in March 2020. However, partial restrictions were lifted much earlier than in India, especially in the case of gyms and swimming pools, i.e. on June 6, 2020 (Górnicka et al., 2020). During times of isolation, Polish athletes had to adapt their training programmes and follow safety protocols to ensure their health and fitness. All of these factors could have increased anxiety; the question is to what extent this contributed to anxiety before and during the competition. Therefore, it is worth examining the level of competition anxiety among athletes of two different nationalities in the post-COVID period.
Both India and Poland have taken their own steps to address the difficulties faced by athletes. However, India is geographically larger than Poland; therefore, the application of restrictions varied and depended on the timing and pattern of the spread of the pandemic in different parts of the country. Some rural or suburban areas had fewer restrictions than cities or metropolitan areas. In Poland, on the other hand, strict government restrictions and quarantine measures were in force everywhere, which may have increased anxiety among Poles (Shpakou et al., 2022). The competitive anxiety largely depended on whether the athletes had a plan to adapt to the changes caused by the lockdown, the extent to which the government or sports authorities provided support to the athlete in terms of facilities, easing of restrictions, state-of-the-art equipment, etc. Few studies have shown the training routine of Indian and Polish athletes during the lockdown (Esht et al., 2021; Shpakou et al., 2022). Some athletes raised concerns through news outlets. For example, some athletes in India have experienced gaps in their training compared to athletes in other countries (Bhattacharya, 2020).
How athletes deal with the resulting anxiety and its long-term personal and social consequences has become a matter of concern (Peteet, 2020). The new (post)pandemic context caused discomfort and uncertainty and affected not only sports calendars but also paths, progress, and attitudes toward sports life. Nevertheless, according to Raglin (1992), many athletes perform at their peak when they are feeling extremely anxious. We still don’t know why some athletes collapse under pressure while others do not, and we still know very little about the neurological underpinnings of pressure-induced performance declines (Masaki et al., 2018). This COVID-19 pandemic encouraged us to look into the situation of sports players regarding their levels of competitive anxiety and its determinants, because now it is even more complicated, as all the restrictions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic were lifted from Poland on 28th March 2022 and from India on 31st March 2022. After this period, we can call it the post-COVID world where we study the impact of the pandemic on sports players and whether it affects their performance. However, even after the restrictions were lifted, the COVID-19 virus continues to spread around the world, impacting lifestyle changes. With the lockdown, isolation, and social restrictions, many athletes are also facing problems of weight gain. Studies have shown that changes related to COVID-19 have worsened the food-body relationship in athletes (Buckley et al., 2021). In the overall population, studies have shown that since COVID-19 began, there have been perceived increases in body weight, eating, and screen time, as well as a reduction in physical activity (Jia, 2021; Keel et al., 2020) and the preference to spend more time at home now than before COVID-19 (Zachary et al., 2020) provoked us to find out if the same scenario is going on with the athletes too. Therefore, we decided to evaluate the level of competitive anxiety in sports players of two different cultures and to determine whether there is a pattern between the levels of competitive anxiety of sports players, their BMI, and the frequency of sports training in the post-COVID world. This study will fill a gap in the literature on cross-cultural research in sports psychology and provide more evidence on the performance of sports players in the post-pandemic era.
PURPOSE OF THE STUDY
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the levels of competitive sports anxiety between Indian and Polish sports players in the post-COVID world. Due to the restrictions and social blockages following the COVID-19 epidemic, it was observed that young people had an increase in body weight with a decrease in physical activity. We sought to determine the level of sports anxiety in athletes and whether it is related to their BMI and the frequency of their physical activity in the post-COVID era.
The following research hypotheses were formulated:
H01: There is no significant difference between the Indian and Polish sports players regarding the level of competitive anxiety.
H02: There is no significant difference in the level of competitive anxiety between Indian and Polish sports players regarding BMI scores.
H03: There is no significant difference in the frequency of sports training between Indian and Polish sports players regarding BMI scores.
PARTICIPANTS AND PROCEDURE
DESIGN
The objective of this cross-cultural study between Indian and Polish sports players is to assess the association of trait anxiety, worry, concentration disruption, and somatic trait anxiety in relation to the frequency of sports training and BMI scores during post-COVID times.
PARTICIPANTS
The subjects of the study were sports players recruited through purposive sampling. Fifty sports players (playing variety of sports modalities) in two independent samples each were successfully recruited from the Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education, Gwalior, India (n = 50; F = 50%, M = 50%), and the Department of Physical Culture and Sports at Kazimierz Wielki University, Bydgoszcz, Poland (n = 50; F = 50%, M = 50%). Their participation was voluntary. They were given the consent form and briefed about the study and the procedure. A paper-and-pencil assessment was conducted. The age range of the participants was 18-30 years (Indian athletes: M = 23.65, SD = 2.75; Polish athletes: M = 23.50, SD = 3.27). They belong to one of the following levels of participation in sports: collegiate (India = 8, Poland = 9), state (India = 18, Poland = 16), national (India = 17, Poland = 18), and international (India = 7, Poland = 7).
The inclusion criteria were that athlete should have been involved in their respective sports for more than 2 years and age should be 18 years or above.
PROCEDURE
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All participants were informed in detail about the purpose and objectives of the study so that they could give well-considered and voluntary consent to participate. After completing the consent form, the study procedure began.
MEASURES
Weight and height of the participants were measured and then BMI was calculated with the Quetelet equation [body mass (kg)/height (m2)]. The results were interpreted according to the WHO criteria: underweight (BMI < 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5 kg/m2 ≤ BMI < 25.0 kg/m2), overweight (25.0 kg/m2 ≤ BMI < 30.0 kg/m2), and obesity (BMI ≥ 30.0 kg/m2) (Branca et al., 2007).
Before filling in the questionnaire, participants of both countries completed a sociodemographic data form. The participants were asked about gender, age, education, domicile, game, frequency of training, and level of participation in sports. Participants were also asked if they had any prior medical or psychological issues.
Sport Anxiety Scale-2. Polish participants completed the Sport Anxiety Scale-2 (SAS-2; Tomczak et al., 2022). It consists of 15 items that make up 3 subscales (somatic anxiety, worry, and concentration disruption), with 5 items each. Respondents give answers on a Likert scale from 1 (not at all) to 4 (very much) to estimate how they usually feel during or before sports competitions. The minimum score is 15 and the maximum is 60. The scale has high internal consistency coefficients (α = .92). The alpha coefficients for the subscales somatic anxiety, worry, and concentration disruption were .84, .91, and .81, respectively.
Participants from India also completed the Sport Anxiety Scale-2 (SAS-2; Smith et al., 2006). In the Indian sample, the scale has high internal consistency coefficients (Cronbach’s α = .91) too. The alpha coefficients for the subscales somatic anxiety, worry, and concentration disruption were .89, .91, and .84, respectively. The scale has an acceptable test-retest reliability index (ICC = 0.87).
DATA ANALYSIS
IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows version 29.0 was used for the data analysis process. The responses of Indian and Polish athletes were compared using a t-test for independent samples. DATAtab: an online statistics calculator was used to create graphs. Statistical significance was set at p < .05.
RESULTS
DEMOGRAPHIC PROFILE OF PARTICIPANTS
Descriptive statistics of the measured variables (age, weight, height, education, place of residence, and frequency of training) are shown in Table 1. The mean value of age for the Polish sample was 23.50 (SD = 3.27) and for the Indian sample 23.65 (SD = 2.75). The mean values of weight for the Polish and Indian samples were respectively 72.01 (SD = 12.67) and 70.31 (SD = 7.98). The mean value of height for the Polish sample was 172.16 (SD = 9.93), and for the Indian sample 174.85 (SD = 9.49).
Table 1
Sociodemographic data for Polish (n = 50) and Indian (n = 50) sports players
Polish and Indian sports players are differentiated according to BMI categories. The obtained results are presented in Table 2.
Table 2
BMI categories for Polish and Indian samples
Further analyses consisted of a test of the significance of differences in the overall anxiety score, its subscales, and BMI values for both samples. The obtained results are presented in Table 3.
Table 3
Comparison of competitive anxiety and BMI between India and Poland
The level of anxiety in the two studied samples was found to be significantly different. The same was true for three sub-scores of the anxiety scale: somatic trait anxiety, worry, and concentration disruption. Thus, the null hypothesis (H01) was rejected.
The t-value of the BMI score for India and Poland was –2.64, with a significance of .01. Overall, the BMI of Polish sports players (M = 24.61) was higher than Indian sports players (M = 22.78).
Regarding gender, the BMI of Polish female sports players (M = 24.70) was higher than that of Polish male sports players (M = 24.52), while the opposite was found in India. Indian male sports players (M = 23.26) had higher BMI than their female counterparts (M = 22.29).
In terms of BMI, most Indian sports players fell into the normal category (n = 44), while Polish sports players are categorized in all BMI categories. Although the majority of Polish sports players were of normal weight, as many as 19 of them were categorized as overweight (n = 11) or obese (n = 8); see Table 2.
For testing hypothesis H02, the two-factor analysis of variance with repeated measures showed an interaction between nationality, the total score of anxiety, and BMI (p = .001); see Table 4. Thus, the null hypothesis (H02) was rejected.
Table 4
Two-factor ANOVA with repeated measures
For testing hypothesis H03, the two-factor ANOVA without repeated measures showed a significant difference between the groups of the independent variable nationality in relation to the dependent variable BMI (p = .007), and also that there was a significant difference between the groups of the independent variable frequency of sports training in relation to the dependent variable BMI (p = .001) but no interaction was found between the two variables nationality and frequency of sport training in relation to the dependent variable BMI; p = 1.00 (see Table 5). Thus, the null hypothesis (H03) was not rejected.
Table 5
Two-way ANOVA without repeated measures between frequency of sports training, BMI, and nationality
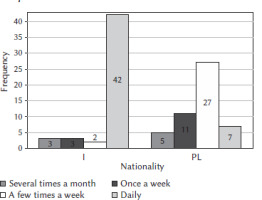
The frequency of sports training of the sports players was categorized as several times a month, once a week, a few times a week, and daily (see Table 1). The majority of the Indian sports players trained in their respective sports daily (n = 42), while the majority of the Polish sports players trained in their respective sports a few times a week (n = 27).
Female sports players’ levels of sports anxiety (M = 22.72) in the Indian population are higher than male sports player’s sports anxiety (M = 21.88), and in Poland, male sports player’s levels of sport anxiety (M = 28.84) are higher than female sports player’s sports anxiety (M = 28.36). Although the difference is not vast, the overall level of sports anxiety is higher in Polish sports players (M = 28.60) than in Indian sports players (M = 22.30).
In Table 6, it can be seen that most of the national and state-level athletes in India were training daily in the post-COVID times. In Poland, most of the national level athletes were training a few times a week in the post-COVID times.
Table 6
Frequency of sports training for different levels of sports career
DISCUSSION
The purpose of this study was to assess the competitive anxiety of Polish and Indian sports players in the post-COVID world (i.e., after March 2022, when COVID-19 restrictions ended to some extent). We looked for any patterns between levels of competitive anxiety, BMI, and frequency of sports training and whether these differed between India and Poland. Studies showed that individuals (aged 18-29) displayed significantly higher levels of anxiety during the pandemic, with a mean value for the total sports anxiety score of M = 38.73 (Irfan & Singla, 2022); M = 40.38 for Polish athletes (Shpakou et al., 2022). In contrast, our study showed that the mean values of the total score of anxiety for Indian and Polish sports players were 22.30 and 28.60, respectively, which are low levels of sports anxiety; it means that sports players in both cultures were not feeling that much competitive anxiety in this post-pandemic time. The data for this research were collected from August to October 2022. Our values are similar to the results obtained before the pandemic, when the mean values for archers’ and shooters’ competitive anxiety were 20.90 and 23.50 (Singh et al., 2019).
The reason for the shift in level of anxiety could be that during the pandemic, athletes faced lots of challenges, competition cancelation, not going to the locker room, and frequent training stoppages due to teammates or coaches testing positive for COVID (González-Hernández et al., 2021). Meanwhile, now that the restrictions have been lifted and everyone is vaccinated, they feel less anxiety than during the pandemic. Athletes were able to adapt rather quickly and continue their physical activity (Shpakou et al., 2022). We can assume that this result could be because of the adaptability and resilience characteristics of the sports players. Very similar results were documented by researchers who conducted a validation study of SAS-2 among Polish athletes (Tomczak et al., 2022). They reported a mean value for the total sports anxiety score for high-performance athletes (M = 26.35), which is very close to our result for Polish sports players (M = 28.60).
We found a significant difference between the total sports anxiety score of Indian sports players and Polish sports players, t(73.41) = –4.28, p < .001. According to Zachary et al. (2020), roughly 22% of adults were reported to have gained weight during the pandemic. Lack of sleep, decreased physical activity, snacking after dinner, eating in response to stress, and eating because of the appearance and smell of food were behaviours linked to weight gain during self-quarantine for common people. Undoubtedly, this interpretation could be true for the athletes too, as the pandemic has also changed many athletes’ behaviour, which could be visible in our results regarding high BMI scores leading to higher total sports anxiety scores in the Polish sample. According to Sidor and Rzymski (2020), 43.5% of Polish respondents reported eating more during quarantine, and 51.8% of respondents were snacking between meals more frequently. This result is also supported by the WHO European Region’s report on obesity (WHO, 2022) stating that the prevalence of obesity tends to be higher in richer countries across Europe, North America, and Oceania. The highest levels of both overweight and obesity are found in the Mediterranean and eastern European countries, which supports our results regarding higher BMI values in the Polish sample.
We assumed that higher BMI values might be related to the frequency of sports training for sports players. The results showed a significant difference between Indian and Polish sports players in relation to BMI. There was a significant difference between the groups of frequency of sports training in relation to BMI. However, no interaction between the two variables nationality and frequency of sport training in relation to BMI was found (see Table 5). The interaction between the frequency of sports training and nationality in relation to BMI is not in line with the literature. For example, there are differences in the organization of the training sessions, their frequency, and duration between Poland and China (Lenartowicz & Ciok, 2020). Chinese athletes reportedly had long and intensive training sessions, which could be one or two sessions daily on workdays, and sometimes they had to train on weekends, too. Meanwhile, the number of training sessions in Poland does not exceed three per week, and these can last two hours a day. Although there was a significant difference between the frequency of sports training and BMI (see Table 5), the discrepancy in results may also be due to the limited sample. However, even in this small sample, among Indian athletes, the typical frequency of training was described as “daily” (n = 42), while Poles typically stated that they trained “a few times a week” (n = 27) (see Figure 1). Therefore, the frequency of training sessions might also affect the BMI score of the athletes. This is consistent with the findings of the China Kadoorie Biobank study and the European Kardiovize Brno 2030 Study, in which greater physical activity was related to a lower BMI (Agodi et al., 2018; Du et al., 2013). Also, a shift in training intensity from vigorous to mild and a reduction in the total duration of training sessions per day from 17% to 3% had been observed among 18- to 35-year-old male national players in India during the pandemic (Esht et al., 2021). However, our results in the post-COVID time show that most of the national players in India are training daily, as they have already adapted to the pandemic situation and are training rigorously for their next competition. In Poland, studies showed that athletes adapted the training routines at home. Players in some sports, such as cycling, maintained their volume and frequency of training during the pandemic; however, they reduced the intensity of training by lowering the time spent on high-intensity intervals (Rzymski et al., 2022). In our results, Polish players were training a few times a week, which is similar to the results in pre-pandemic times (Lenartowicz & Ciok, 2020).
Thus, even though the score of competitive trait anxiety was lower in both the Polish and Indian samples, comparatively the competitive trait anxiety of Polish sports players was higher than Indian sports players in each subscale of SAS-2. Probably it was because of the higher values of BMI, which might have resulted from the lower frequency of sports training. Some studies positively associate psychosocial stress with all BMI levels (Eik-Nes et al., 2022). However, other studies have found an inverted U-shaped relationship, where lower levels of anxiety are associated with both low and very high BMI, and high levels of anxiety are associated with medium to high BMI (Haghighi et al., 2016). Obesity is reported to be a risk for anxiety disorders (de Wit et al., 2022). The levels of competitive anxiety are not high in both countries, perhaps because the athletes have already adapted to the pandemic. However, certain changes, such as isolation rules in both countries, may differ for example in India depending on the specific location, and the surge in COVID-19 cases (i.e. less in villages and towns, and more in city and metropolitan areas; OECD, 2021). Lower numbers of cases were reported in India, where urbanization was less than 20% (Gupta et al., 2022). Similarly, in Poland, population density is an important factor influencing the high number of infections in the region (Parysek & Mierzejewska, 2021). Therefore, cases of obesity or overweight athletes in the city or metropolitan cities in Poland show a relation with studies during the pandemic, where urban places were associated with easy access to fast food and ordering meals frequently, even during quarantine. It was reported that there was a decrease in the consumption of homemade meals in Poland (Górnicka et al., 2020), while in India, homemade meals were preferred. This could be a cultural issue, as cooking at home is usually preferred in India. Also, studies showed that there was an increase in the frequency of cooking as well as in the number of meals during the day because all family members were at home (Menon et al., 2022). However, an increase in the daily food intake by 20% of the total athletes was reported despite the decrease in physical activity (Esht et al., 2021). Also, according to Sidor and Rzymski (2020), 43.5% of Polish respondents reported eating more during quarantine, and 51.8% of respondents were snacking between meals more frequently.
One of the advantages of this study is that the results of trait anxiety were compared with previous studies having similar samples for the levels of trait anxiety of Indian and Polish athletes separately. The other advantage is to be able to bring those factors to light which affected the athletes of both countries, i.e., India and Poland, in the pandemic situation. It is a good result that they do not have high levels of competitive anxiety, but these factors might be useful to plan for an upcoming epidemic.
A limitation of this study was not measuring body mass composition. Also, there was a lack of data before and during the pandemic; the availability of data before and during the pandemic would have allowed good comparison of results. Small sample size is another limitation of the study. More cross-cultural research work on the possible connection between competitive trait anxiety, BMI, and frequency of sports training is required in the sport psychology discipline, especially in the post-COVID world, to determine whether the athletes are undergoing some behavioural or psychological changes due to the pandemic.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study attempted to identify potential patterns between competitive trait anxiety, BMI, and frequency of sports training in a cross-cultural context in the post-COVID world. We found that levels of competitive trait anxiety were lower than the levels of competitive trait anxiety found in studies conducted during the pandemic times. We encountered significant differences in the levels of competitive anxiety between Indian and Polish sports players. Indian sports players had lower levels of competitive anxiety. Our results are consistent with the post-COVID literature on weight gain in young people especially in the Polish population due to the perpetuation of sedentary habits after repeated lockdowns and other sanitary restrictions. The relation between the frequency of sports training and BMI was significant, but when compared in different cultures, in this context India and Poland, their association was not significant. It could be due to the smaller number of participants (n = 50) in each group, which is also a limitation of this study. However, further research is necessary to assess the late impact of the pandemic on the lives of sports players as these costs are accompanied by many others localized in the psychological sphere of young athletes, which are only becoming apparent in the post-pandemic world.